Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
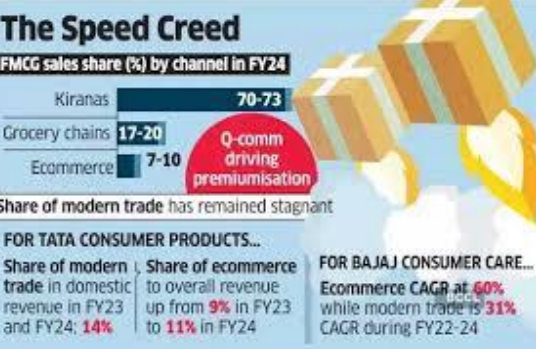
The Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) sector is witnessing a structural shift as Quick Commerce (qcomm) evolves from a niche convenience service into a mainstream distribution powerhouse. Historically reliant on \'Kirana\' stores (General Trade), legacy players like HUL, Marico, and Tata Consumer are now recalibrating their supply chains to serve the hyper-local, 10-minute delivery market. Key Summary Points• Strategic Revenue Shift: Q-comm now contributes significantly to the growth of legacy giants; for instance, it accounts for nearly 20% of Emami’s e-commerce business and around ₹1,800 crore of HUL’s annual revenue. • Rapid Market Penetration: The sector is projected to grow at a CAGR of 37-39% between 2025 and 2030, potentially reaching a market value of ₹5.8 trillion. • Urban Consumer Dominance: The model thrives on high-density urban clusters, catering to 51 million monthly transacting users (as of 2025) who prioritize speed for staples and impulse purchases. • Portfolio Diversification: Beyond daily essentials, FMCG firms are using q-comm to scale high-margin \'Direct-toConsumer\' (D2C) brands in premium personal care and health foods. • Operational Overhaul: To succeed, companies are moving away from traditional warehousing toward \'Dark Store\' optimization and focused teams to manage real-time inventory. • Capital Intensity and Barriers: The model’s high infrastructure costs favor established FMCG players with deep pockets, creating a competitive advantage over smaller, regional competitors. Definitions of Key Terms • Quick Commerce (Q-Comm): A subset of e-commerce focused on ultra-fast delivery (typically under 30 minutes) of small quantities of goods, facilitated by local \'dark stores.\' • Dark Stores: Micro-fulfillment centers located in high-demand urban areas that are not open to the public and serve exclusively as hubs for online order picking. • General Trade (GT): The traditional retail channel in India, consisting of neighborhood Kirana stores and small independent retailers. • SKU (Stock Keeping Unit): A unique identifier for each distinct product and service that can be purchased, used by firms to track inventory. Constitutional and Legal Provisions • Consumer Protection (E-Commerce) Rules, 2020: Governs the responsibilities of e-commerce entities, ensuring transparency in pricing, expiry dates, and country of origin. • Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Policy: FDI in multi-brand retail is restricted, but 100% FDI is permitted in the marketplace model of e-commerce, which most q-comm players utilize. • Competition Act, 2002: Relevant in monitoring \'predatory pricing\' or \'deep discounting\' practices that might arise as q-comm platforms compete with traditional brick-and-mortar stores. • Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities) Rules: Mandates that all pre-packaged commodities sold via e-commerce must display essential declarations like MRP and net quantity. Additional Key Points • Impact on Kirana Stores: While q-comm is growing, it is unlikely to fully replace General Trade, which still holds the lion\'s share of rural and semi-urban Indian retail.• Sustainability Concerns: The rapid delivery model increases the carbon footprint due to frequent small-batch deliveries and high packaging waste. • Employment Generation: The sector is a massive driver of gig economy jobs, specifically for delivery partners, though labor welfare remains a point of debate. Conclusion Quick commerce has transitioned from a pandemic-era luxury to a fundamental pillar of India’s retail architecture. For FMCG companies, it represents a \'high-velocity\' channel that captures the impulsive and time-poor urban consumer. However, the long-term viability of the sector will depend on balancing capitalintensive logistics with sustainable profitability and ensuring fair competition with traditional retail ecosystems. UPSC Relevance • General Studies II: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors (Ecommerce regulations and FDI policy). • General Studies III: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, and growth; Changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth. • Mains Perspective: Analyze the impact of the gig economy and rapid urbanization on India\'s retail landscape and the socio-economic implications for traditional small-scale traders.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com