Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
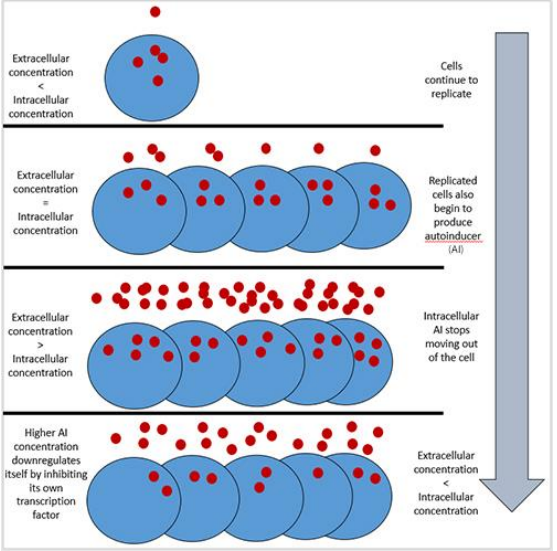
Molecular biologist Bonnie Bassler has highlighted the revolutionary potential of \'bacterial communication,\' describing microbes as multilingual entities capable of collective behavior. This research shifts the perspective on bacteria from mere pathogens to essential biological partners with immense promise in medicine, agriculture, and environmental science. Key Highlights of Bacterial Communication • Quorum Sensing Mechanism: Bacteria use a chemical language to communicate and coordinate their behavior based on population density, a process known as \'quorum sensing.\' • Multilingual Capabilities: Microbes are \'multilingual,\' using specific chemical signals for their own species and a \'universal\' language to communicate with different bacterial species. • Medicinal Paradigm Shift: Understanding these chemical signals allows for the development of \'anti-quorum sensing\' therapies, which could replace or supplement traditional antibiotics by \'silencing\' bacterial coordination. • Symbiotic Relationships: Many bacteria exist in vital symbiotic states, such as the Vibrio fischeri providing bioluminescence to squids or the gut microbiome facilitating human digestion and nutrient absorption. • Collective Evolution: Bacterial communication provides a window into how collective behaviors and multicellularity evolved on Earth, suggesting that complex life shares foundational traits with these \'magical microbes.\' • Pathogenic Coordination: Deadly bacteria like Vibrio cholerae (cholera) rely on quorum sensing to time their attack on the host, ensuring they only produce toxins when their numbers are sufficient to overwhelm the immune system. Constitutional & Legal Provisions • Article 51A(h): The Indian Constitution mandates that it is a fundamental duty of every citizen to develop \'scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform.\' • Biological Diversity Act, 2002: Regulates access to biological resources and associated knowledge, ensuring equitable sharing of benefits arising from the use of microbes found in Indian territory. • National Biotechnology Development Strategy: A policy framework by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) that prioritizes research in microbial technologies for healthcare and sustainable agriculture. • Patent Act, 1970: Specifically Section 3(j), which excludes certain biological processes from patentability, though it allows for patents on innovative microbial applications and formulations. Definitions of Key Terms • Quorum Sensing: A cell-to-cell communication process that allows bacteria to share information about cell density and adjust gene expression accordingly.• Bioluminescence: The production and emission of light by a living organism, often used by bacteria like Vibrio fischeri in symbiotic relationships. • Gut Microbiome: The complex community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that live in the digestive tracts of humans and assist in metabolism. • Anti-Quorum Sensing (Quorum Quenching): A therapeutic approach that disrupts bacterial communication to prevent them from launching a coordinated attack, thereby reducing virulence without necessarily killing the bacteria. Conclusion The discovery that bacteria are \'social\' organisms challenges the traditional \'kill-all\' approach of antibiotics. By decoding their chemical languages, science can move toward precision medicine and sustainable biotechnological solutions. This transition from viewing bacteria as solitary enemies to understanding them as sophisticated, communicative networks marks a new frontier in biological sciences. UPSC Relevance • Prelims: Science and Technology—Basic biology, concepts of symbiosis, bioluminescence, and the mechanism of antibiotics vs. anti-quorum sensing. • Mains (GS Paper III): Developments and their applications and effects in everyday life; Achievements of Indians in science & technology; Indigenization of technology and developing new technology; Issues relating to intellectual property rights and biotechnology.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com