Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
UNSC Reforms
News: UN General Assembly (UNGA) President Csaba Korosi has expressed concern that the UN Security Council does not reflect today’s realities, is paralysed and is unable to discharge its basic function of maintaining international peace and security.
What concerns were raised?
The General Assembly has always been very much divided. Among the 193 countries, there are five negotiating groups and they are neutralising each other.
The functioning of the General Assembly is as much important as the permanent members of the UNSC in ensuring reform of the United Nations system.
The permanent members were “historically not enthusiastic” about reform of the UN system but they have all agreed that it is necessary for introducing changes in the Security Council.
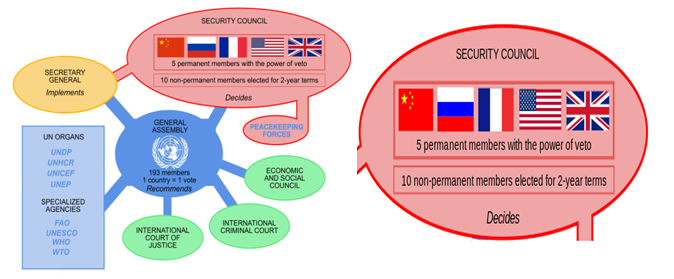
What is UNSC?
It is one of the UN’s six main organs and is aimed at maintaining international peace and security.
Headquarters – New York City.
UNSC has 15 members: 5 permanent members (P5) and 10 non-permanent members elected for 2-year terms. The 5 permanent members are - United States, Russian Federation, France, China and the United Kingdom.
Why is there growing need for reforms in UNSC?
Since 1945, the world has changed significantly - The Cold War strategic influences have declined; the membership of the UN has increased almost fourfold and the expectations of what the UN should do have grown.
There is a huge European bias in P-5 due to the presence of the United Kingdom and France, including Russia.
Misuse of Veto Power to put national interests ahead of global interests. Critics of the veto power say that it is the most undemocratic element of the UN and the main cause of inaction on war crimes & crimes against humanity.
The geopolitical rivalry among the permanent members has prevented the UNSC from coming up with effective mechanisms to deal with global issues.
Regions like Latin America, the Caribbean Group, the Arab World, and Africa do not have a single permanent member.
As the principal organ of international peacekeeping and conflict resolution, the UNSC is responsible for keeping peace and managing conflict. Its decisions (referred to as resolutions) are binding on all member countries, unlike the General Assembly's. This means that any state's sovereignty can be encroached upon if necessary by taking action, such as imposing sanctions.
Only China is representative of the global south region, whereas the global north has four nations to represent them at the UNSC.
Geopolitical conflict, climate change, food and energy insecurity, and pandemics have brought out the inequities and inadequacies of the way the world currently functions. For example, rising food inflation and shortage of wheat around the world due to Rusia-Ukraine War.
What should be the way forward?
Address the power imbalance between P5 countries and other UNSC member countries.
Changing global dynamics need a change in status quo. UNSC must expand its permanent and nonpermanent seats to address complex issues world is facing.
Equitable representation of all the regions in the UNSC is critical to decentralizing its governing power and authority over nations.
What steps must India take?
India as current non-permanent member can start by drafting a resolution containing a comprehensive set of proposals for reforming the UNSC.
In September 2022, India made a push for UNSC reform hosting a meeting of two separate groupings – G-4 and L 69 – in New York on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly.
As India leads Global South, it needs to revitalise its engagement with its traditional partners in the “global south” by articulating their peace and security concerns in the UNSC.
Conclusion
India advocates for democratic reforms in multilateral fora. It believes that if UNSC is made for representative, approachable, efficient and effective than it will not only be better responsive but also earn the respect of developing countries for making efforts to reform and change.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com