Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Nagorno-Karabakh conflict and India
News: Recently, Azerbaijan forces launched an offensive mission and declared victory over the separatist province of Nagorno-Karabakh.
About Nagorno-Karabakh:
• Nagorno-Karabakh is a mountainous region officially recognised as part of Azerbaijan.
• But its 1.2 lakh population is predominantly ethnic Armenian. Basically, NagornoKarabakh is an ethnic Armenian enclave in Azerbaijan.
• The Armenians are Christians, while Azeris are Muslims..jpg)
Background of the conflict:
• When Czarist Russia gave way to the Soviet Union in 1921, Nagorno-Karabakh was part of the Azerbaijan SSR (Soviet Socialist Republic).
• As the Soviet Union collapsed, the first round of tensions over Nagorno-Karabakh began in 1988, with its regional legislature passing a resolution declaring its intention to join Armenia, despite being geographically located within Azerbaijan.
• When the Soviet Union was dissolved in 1991 and Armenia and Azerbaijan achieved statehood, NagornoKarabakh officially declared independence.
• In 1993, war broke out and Armenia had captured Nagorno-Karabakh.
• In 1994, Russia brokered a ceasefire known as the Bishkek Protocol. “This made Nagorno-Karabakh de facto independent with a self-proclaimed government in Stepanakert, but still heavily reliant on close economic, political, and military ties with Armenia.
• In September 2020, Azerbaijan and Armenia went to war again. However, Azerbaijan managed to wrest control of the territory around Nagorno-Karabakh.
What is the present position?
• Right now, Azerbaijan forces have gained prominent control over the region and authorities have said the ethnic Armenian enclave would dissolve on 1st January, 2024.
What is India’s position on the war? What stakes do we have in the region?
• India has ties with both Armenia and Azerbaijan and has maintained that any lasting resolution of the conflict can only be achieved peacefully through diplomatic negotiations.
• Armenia publicly endorses India’s position on the resolution of the Kashmir issue on a bilateral basis and supports India’s aspiration for a permanent seat in the expanded UN Security Council.
• In 2022, the India-Armenia deal to supply Armenian armed forces with PINAKA multi-barrel rocket launchers (MBRL), anti-tank munitions, and ammunitions and warlike stores worth US $250 million was viewed as Delhi siding with Yerevan.
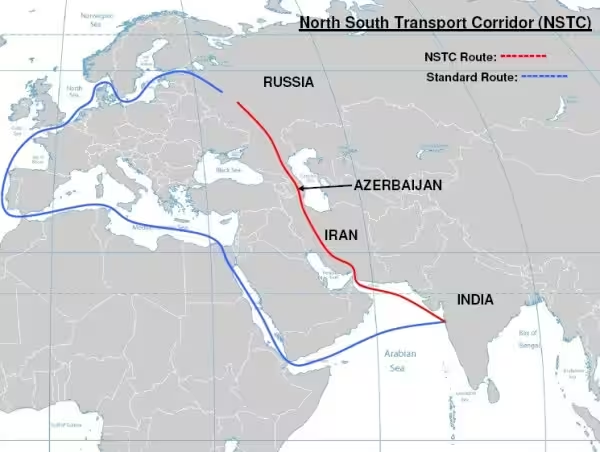
• Armenia and Azerbaijan are members of the International North South Transport Corridor (INSTC), which India is keen to develop. India supports Armenia’s proposal to include Iran’s Chabahar port in INSTC.
• The region is important as a viable corridor for India’s connectivity with Russia and Europe through Central Asia and Iran.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com