Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
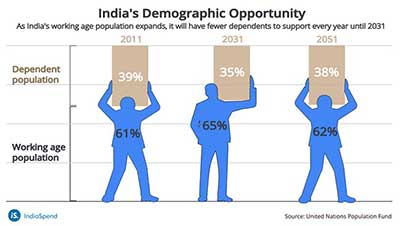
How to reap the Dividend?
Background:
• The editorial focusses on Demographic Dividend, it’s benefits, challenges in reaping the Demographic dividend and some of the Government initiatives taken.
• The topic forms important part of the examination and having necessary data and clarity around it is important.
What is Demographic Dividend?
• Demographic dividend is the economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population’s age structure.
• It occurs when the proportion of working people in the total population is high because this indicates that more people have the potential to be productive and contribute to growth of the economy.
• India’s average age is 29 years, whereas the average age in US, China, France, Germany and Japan is 38, 38, 42, 45 and 48 years, respectively.
• India is in a phase where its working-age population is rising and the old-age dependency ratio is coming down. For example, India’s old-age dependency ratio will reach 37 per cent in 2075, whereas the same will be 55.8 per cent in France, 75.3 per cent in Japan, 49.3 per cent in the US.
• India is the youngest among the most populous countries in the world.
What are the benefits of Demographic Dividend?
• Increase in Economic growth rate – More people part of productive work force, more economic activities, higher working age population and reduced spending on dependent population.
• Increase in labour force – more input for labour force, increased competitiveness, can help in bridging manpower shortage.
• Increase in savings and investment - Demographic dividend can create an incentive for the working population to save more for their future retirement, which can increase the domestic savings and investment rates. These savings and investments can be used to stimulate the economy and finance various development projects.
• Increase in human capital - Demographic dividend can enable higher investment per child in terms of education, health and nutrition, which can enhance the human capital, skills and well-being of the future workforce. This can also improve the quality of life and social outcomes for the population.
What are the challenges of Demographic Dividend in India?
• Asymmetric Demography – Growth in the working age group is likely to be concentrated in some of India’s poorest states. So, to reap rewards of Demographic Dividend these states should have potential to create jobs, Human Resources and financial resources.
• Lack of employability – According to Skills India report 2021, only 45.9% of graduates in India are employable.
• Huge Skill Gap – The same report states that only 5% of workforce is formally skilled in India. US – 52%, Japan 80%.
• Gender inequality - India has one of the lowest female labour force participation rates in the world, at 23.3% (latest data). This means that a large section of the potential working-age population is not contributing to the economy.
• Poor performance in Human Development Indicators – HDI – 130th rank/189 countries. India also lags behind in key nutrition indicators!
• Rising unemployment
• 93% of employment in India is absorbed by the unorganized sector, where workers are employed in underpaid jobs. Thus, there is need to upscale many employees in unorganized sector.
How can India reap its Demographic Dividend?
• To create better opportunities for existing labour force and new entrant into the labor market improving their productivity. Focus on skilling, re-skilling and up-skilling of labour force.
• Need to shift major chunk of the 45.5% of the labour force engaged in agriculture with low and negligible labour productivity to more labour intensive and productive manufacturing industries such as textiles, toys, footwear and auto components etc.
• Focus on quality education and health facilities is equally important.
• Address barriers that prevent entry of women in workforce, address issues that limit women’s potential.
What are the government initiatives to reap benefits of Demographic Dividend?
The Government has focused significantly in areas such as Health, education, skill development, infrastructure development, labour laws etc.
Skill Development - PM Kaushal Vikas Yojana, Jan Sikshan Sansthan, National Apprentice Promotion Scheme
Education -Samagra Shiksha, NEP 2020 and Healthcare - PM Jan Aarogya Yojana, PM Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Pariyojana, Swacch Bharat
Manufacturing - PLI Scheme, Make in India, Startup India, Formalization of labor force, Special assistance to MSME sector
Conclusion
• According to the Economic Survey 2018-19, India’s demographic dividend will peak around 2041, when the share of working-age (20-59 years) population is expected to hit 59%. Thus, it is important to focus on labor intensive manufacturing and subsequent structural transformation just like countries like China, Japan, South-Korea did and sustained an almost 10% annual average growth rate.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com