Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Global Pulses Conference
News: The conference was recently held in New Delhi.
Background:
• The conference is organized by the National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Ltd. (NAFED) and the Global Pulse Confederation (GPC).
• The theme for the 2024 World Pulses Day, which is observed every year on 10th February, was “Nourishing Soils and People”
About Conference:
• The Global Pulses Conference is an annual event that brings together key industry players from across the globe to share insights about the pulses market.
• Pulses are annual leguminous crops or seeds of variable size, shape, and color used for both food and feed.
• The conference urged India to augment production of pulses to meet the nutritional requirements.
Pulses in India:
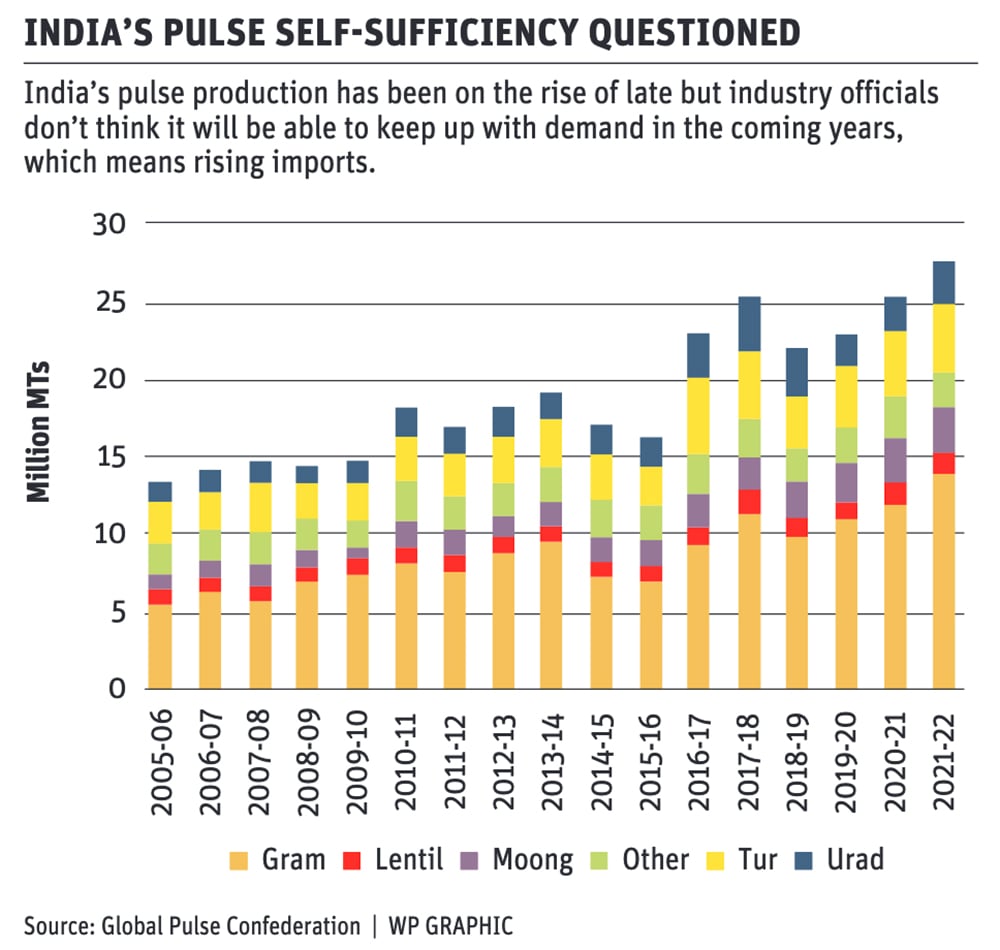
• Production: Pulses production in India reached a record of 26.96 Million Metric Tonnes (MMT) in 2021-22. The area under pulses cultivation increased from 24.91 million hectares in 2015-16 to 30.37 million hectares in 2021-22. The yield also improved from 656 kg/ha to 888 kg/ha.
• Export: In FY23, India exported 775,024.48 MT of pulses worth Rs. 5,397.86 Crores.
• Import: Despite being the leading global producer, India imports a considerable number of pulses to meet the domestic requirement. The import dependency of pulses came down from 19% in 2013-14 to around 9% in 2021-22. It’s projected to drop down further to around 3% by 2030-31.
• Gram (chickpeas) holds the largest share of around 40% in the total production. This is followed by Tur/Arhar (pigeon pea) at 15 to 20%, and Urad/Black Matpe and Moong at around 8-10% each
Benefits of Pulses production:
• Environmental Sustainability: Pulses naturally produce their own nitrogen, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
• Soil Health: Pulses improve soil fertility through their nitrogen-fixing properties. They also increase overall productivity and water use efficiency of all crops in a system while improving efficiency and resilience.
• Nutrition: Pulses are highly nutritious, containing vitamins, micronutrients, and a high protein content. They are also rich in iron, folate, and zinc, which are crucial for good health and eyesight.
• Fodder & Feed: Pulses provide a superior quality of fodder & feed to the cattle, as they are good forage crops with proteins and minerals content.
• Resilient to climate change, additional income for farmers.
What are the factors responsible for low Pulses production in India?
• Absence of High-Yielding Varieties: There is a lack of high-yielding varieties that are resistant to pests and diseases.
• Lack of Assured Market: Farmers often face uncertainty in the market for their produce.
• Ineffective Government Procurement Operations: The operations for government procurement of pulses are often ineffective.
• Preference for Cash Crops: Farmers may prefer cultivating cash crops such as rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
• Vulnerability to Pests and Diseases: Pulses are more susceptible to the vagaries of weather, pests, and disease.
• Difficulty in Developing Varieties: Developing pulse varieties, which are both high-yielding and tolerant of stress and pests, is difficult.
Government of India initiatives:
• Self-Sufficiency Goal: The government aims to achieve self-sufficiency in urad and tur by 2027 through large-scale demonstrations and public-private partnerships.
• Assured Purchase Contract: The government is encouraging farmers to diversify into pulses from traditional crops through an assured purchase contract of five years.
• National Food Security Mission: The Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare is implementing the National Food Security Mission (NFSM)-Pulses with the objectives of increasing production through area expansion and productivity enhancement in all the districts.
• PM-AASHA: To ensure remunerative prices to farmers, Government implements an umbrella scheme PM-AASHA comprising Price Support Scheme (PSS), Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS) and Private Procurement Stockist Scheme (PPSS) in order to ensure Minimum Support Price (MSP) to farmers for their produce of notified oilseeds, pulses and copra.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com