Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Central Govt’s Fiscal Position in line with revised estimates
News: Recently, Data released by Controller General of Accounts showed that the central government’s Fiscal position in just concluded FY 2022-23 was in line with the revised estimates laid out in Union Budget.
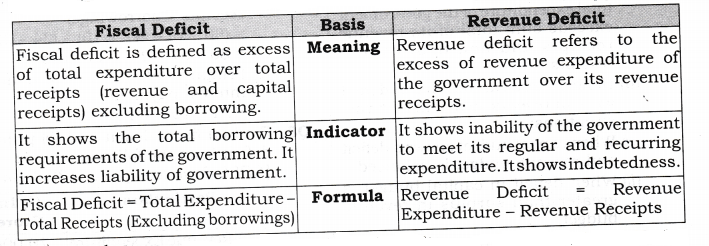
What is Fiscal Deficit?
The difference between total revenue and total expenditure of the government is termed as fiscal deficit. It is an indication of the total borrowings needed by the government.
How was Centre able to contain its fiscal deficit?
On the revenue side, higher tax and non-tax revenues were one of the reasons.
On the expenditure side, the centre cut back marginally on revenue expenditure while maintaining its commitment to enhancing capital expenditure.
The Centre’s Gross tax collections grew at a healthy 12.7% in 2022-23.
On the expenditure side, the centre’s capital expenditure grew by 24%, driven by outlays on roads and railways.
While fertilizer subsidy was higher than budgeted, it was offset by lowering spending in other areas such as the food subsidy.
What is the Government’s target on Fiscal Deficit?
The Finance minister’s aim is to bring down the Fiscal Deficit to below 4.5% of GDP by 2025-26.
What are the ways to Finance the Fiscal Deficit?
Borrowing from domestic sources, such as banks, financial institutions, public sector undertakings, and individuals. This can be done through issuing government securities, treasury bills, bonds, etc
Borrowing from external sources, such as foreign governments, multilateral agencies, private lenders, etc. This can be done through external commercial borrowings, foreign currency loans, sovereign bonds, etc
Printing money or monetizing the deficit. This can be done by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) buying government securities and increasing the money supply in the economy.
Disinvestment or selling off government assets or stakes in public sector enterprises. This can generate non-tax revenue for the government and reduce its expenditure.
Higher Taxation can also help finance Fiscal deficit.
Way forward
Each of the methods (to finance Fiscal Deficit) has its own advantages and disadvantages, such as impact on inflation, interest rates, exchange rates, debt sustainability, growth prospects, etc. The government has to balance these factors and choose the optimal mix of financing sources for its fiscal deficit.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com