Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
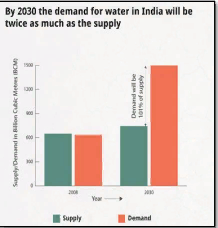
India’s Water Crisis
News: The water scarcity issue has impacted over 7,000 villages, 1,100 wards, and 220 talukas in Karnataka to date.
About:
Water Scarcity Challenges in India
• Facing Severe Water Stress: Despite accommodating approximately 18 percent of the global population, India possesses only 4 percent of the world water resources, as indicated in the NITI Aayog Report of 2017. This places the country among the most water-stressed nations worldwide.
• Inadequate Per Capita Water Availability: Standing at approximately 1,100 cubic meters (m3), India per capita water availability falls significantly below the globally acknowledged water stress threshold of 1,700 m3 per person. Moreover, it dangerously approaches the water scarcity threshold of 1,000 m3 per person.
• Disparity in Distribution: The significance of monsoon rains cannot be overstated, and irregular rainfall patterns exacerbate water stress in numerous regions.
• Challenges in Water Accessibility: A substantial number of people lack access to safe drinking water, resorting to contaminated sources or facing difficulties affording clean water.
• Growing Disparity in Water Supply and Demand: The expanding urbanization and industrialization processes exert considerable pressure on the overall water demand, leading to a significant gap between demand and availability.
Causes of Water Scarcity:
• Escalating Demand: The surge in population and swift urbanization places substantial strain on water resources.
• Overutilization: Aggressive extraction of groundwater for agricultural and industrial purposes depletes aquifers at a rate surpassing replenishment capability.
• Contamination: Industrial discharge and agricultural runoff introduce pollutants to surface water, rendering it unsuitable for consumption.
• Inadequate Infrastructure: Leakage in pipes and canals results in the wastage of valuable water, intensifying the pressure on supplies.
• Climate Variability: Unpredictable weather patterns disrupt monsoons and contribute to the worsening water scarcity scenario.
Measures to Address Water Scarcity:
• Implementation of Circular Water Economy: Aimed at optimizing the use of each liter of water and diminishing the city reliance on external water sources.
• Adoption of Water-Saving Techniques: Introducing efficient methods such as drip irrigation in agriculture to minimize water consumption.
• Conducting Public Awareness Campaigns: Crucial efforts to educate the public about water conservation and sanitation practices.
• Infrastructure Enhancement: Essential upgrades to water treatment plants and distribution networks for improved efficiency.
Sustainable Water Management: Implementing integrated water resource management approaches that take into account the interests of all stakeholders.
Public-Private Partnerships: Accelerating progress through collaborative initiatives involving government bodies, businesses, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
Community Participation: Vital empowerment of local communities to efficiently manage water resources.
Technological Solutions Exploration: Investigating desalination, wastewater treatment, and rainwater harvesting technologies as potential sources of new water.
Key Initiatives and Programs by Government:
• National Water Mission (NWM):
o The primary objective of the NWM is the Conservation of water, reduction of wastage, and ensuring more equitable distribution both across and within States through integrated water resources development and management.
• Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) - 2019:
o Initiated in 2019, this mission strives to provide functional tap connections within the premises of each rural household in India by 2024.
o Furthermore, it aligns with SDG target 6.1, aiming for universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all by 2030.
• Ministry of Jal Shakti - May 2019:
o Established in May 2019, the Ministry of Jal Shakti serves to consolidate interconnected functions related to water management.
• Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABY):
o This scheme targets the enhancement of groundwater resource management in areas accounting for approximately 37 percent of such blocks in the country.
• Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) - 2015:
o Launched as a centrally sponsored scheme in 2015, PMKSY operates with a funding structure of 75:25 percent (90:10 for the north-eastern region and hilly states).
o It aims to improve water efficiency across various sectors, including the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP), providing Central Loan Assistance (CLA) to major and medium irrigation projects in an advanced stage of completion to achieve targeted potential, ultimately saving water and improving efficiency.
• National Aquifer Mapping and Management Programme (NAQUIM):
o Under NAQUIM, groundwater aquifers have been mapped, and management plans have been devised for 80 percent of the country.
• Bureau of Water Use Efficiency (BWUE):
o Established as a facilitator, BWUE plays a role in promoting improved water use efficiency across various sectors such as irrigation, drinking water supply, power generation, and industries throughout the country.
Way Ahead:
• In the case of Narmada Bachao Andolan v Union of India (2000), the Court determined that water constitutes an integral aspect of the right to life as outlined in Article 21 of the Constitution. Consequently, it is our shared duty to guarantee the fulfillment of this fundamental human right.
• The urgency of the water crisis necessitates prompt and collaborative measures. Through the embrace of sustainable methodologies, the advocacy of water conservation, and strategic investments in infrastructure, India has the potential to alleviate the crisis and pave the way for a future secured in water resources.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com