Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
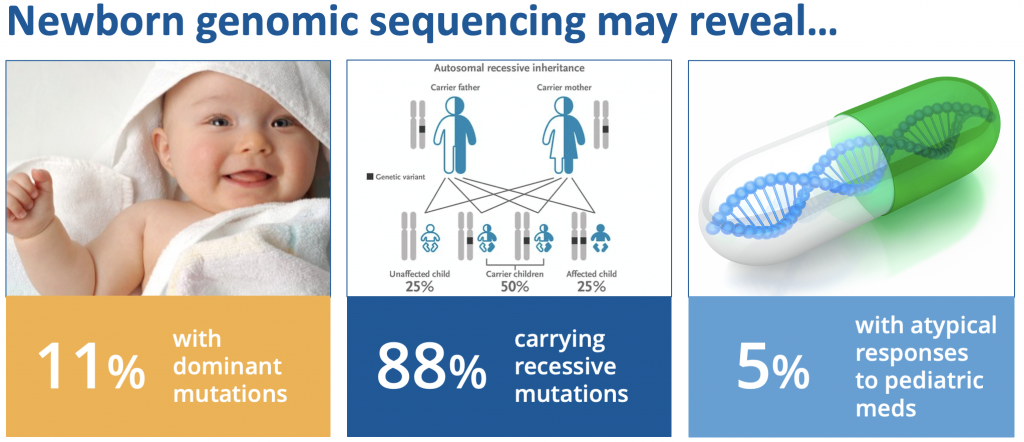
Whole Genome Sequencing
News: Recently, the use of rapid whole-genome sequencing (WGS) in newborns, including healthy newborns, has emerged as a revolutionary approach to diagnose and treat genetic diseases.
What is Whole Genome Sequencing?
• Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) is a laboratory procedure that determines the order of bases in the genome of an organism in one process. A genome is the complete set of genetic information of an organism, which is composed of nucleotide bases (A, T, C, and G). The order of these bases determines the unique DNA fingerprint, or pattern, of an organism.
What steps does it involve?
WGS involves four main steps:
• DNA shearing: Cutting the DNA into small pieces that can be read by a sequencing machine.
• DNA bar coding: Adding small pieces of DNA tags to identify which piece belongs to which organism.
• DNA sequencing: Using a DNA sequencer to identify the bases (A, T, C, and G) that make up each piece of DNA.
• Data analysis: Using computer analysis tools to compare sequences from different organisms and identify differences.
What are applications of WGS?
• Identifying inherited disorders, such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia, by finding mutations or variations in the genome that cause or increase the risk of disease.
• Characterizing the mutations that drive cancer progression, such as changes in the genome that make cells grow faster, spread more easily, or resist treatment.
• Tracking disease outbreaks, such as foodborne illnesses or infectious diseases, by finding similarities or differences in the genomes of pathogens that can indicate their source, transmission, or evolution.
Why sequence newborn Genomes?
• Improving diagnosis and treatment: WGS can help identify rare or complex genetic conditions that may otherwise be missed or misdiagnosed by conventional tests.
• Providing information for future health: WGS can provide information about the risk of developing diseases later in life, such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s, or heart disease.
• Advancing research and knowledge: WGS can generate large amounts of data that can be used for research and discovery. WGS can help understand the causes and mechanisms of genetic diseases, identify new genes and variants, and develop new tests and treatments.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com