Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Utilizing potential of Helium Reserves
News: Recently, researchers have proposed a new model to tap into helium reserves to address shortage issues. Recent new study suggests that reservoirs of this gas, with no carbon footprint, likely exist in geological formations beneath the Earth.
About the Model:
The gas can be produced and stored in crystalline basement rocks, dense rocks that extend from the mantle to the near-surface or surface. These rocks naturally contain uranium and thorium, both of which decay to form helium naturally.
These rocks are 30-40 kilometer thick. They have also existed for millions or billions of years, allowing large amounts of helium to be produced and stored.
These rocks could also be a source of hydrogen. The model showed that energy generated from the radioactive decay of uranium and thorium could split water to form hydrogen.

Key Facts about Helium:
Helium is a noble gas and has a closedshell electronic configuration, making it stable and unreactive.
Helium is the second most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen. However, it is relatively rare on Earth, with most of it being produced by the decay of radioactive elements in the Earth's crust.
As of 2022, USA has largest reserves of helium followed by Algeria and Russia. (World Helium reserves as shown in image are based on 2017 Data and are for reference purpose only)
India’s Rajmahal volcanic basin in Jharkhand is the storehouse of helium trapped for billions of years.
There is currently a shortage of helium in the world owing to factors such as shutdown of some helium plants, the increasing demand for helium in emerging economies, and the lack of new helium sources.
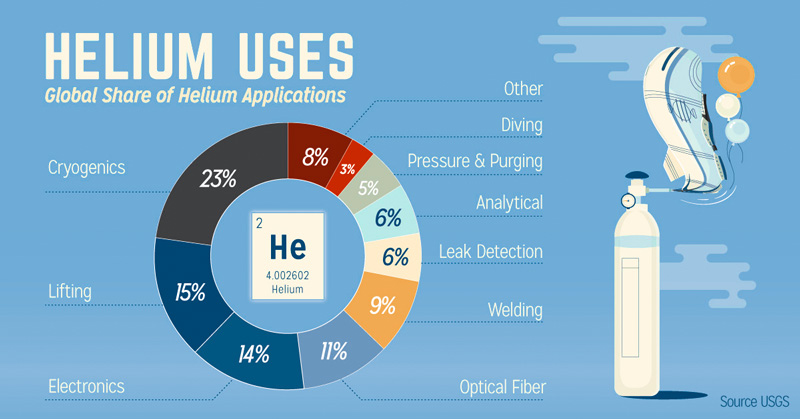
Application of Helium:
Balloons and airships (as it is lighter than air and does not react chemically with other elements).
Industrial applications, including welding, cooling, and as a protective gas in the production of semiconductors and fiber optic cables.
In medical applications, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as a cooling agent for superconducting magnets.
It is also used in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and as a carrier gas in gas chromatography.
Way Forward
The proposed model for tapping into carbon-free helium reserves could provide a sustainable and costeffective solution to the current helium shortage, with the added benefit of hydrogen production.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com