Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
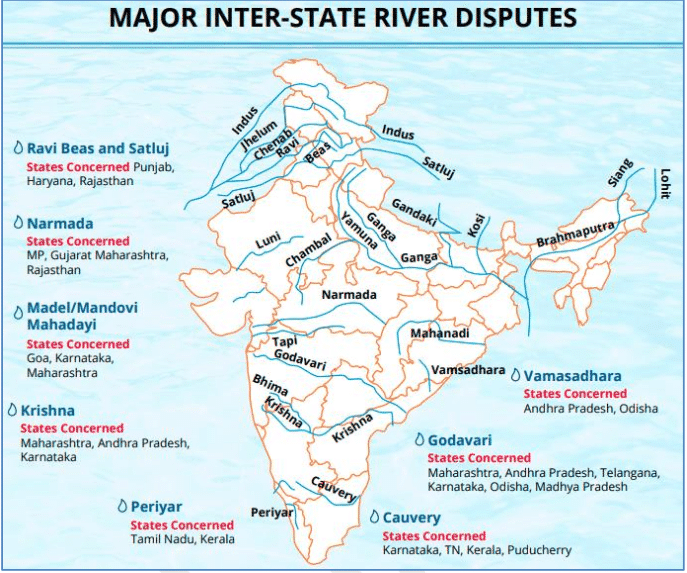
Inter-state water disputes
News: Recently, a meeting was held between the Chief Ministers of Punjab and Haryana in the presence of the Union Jal Shakti Minister.
Why was the meeting held and what is the issue?
• It was held to resolve the Sutlej-Yamuna Link Canal dispute.
• The dispute between Punjab and Haryana has been festering since the 1960s, and various efforts to resolve the issue have failed. This dispute is not an isolated case. A lot of Inter-State Water Disputes have been festering among various States for a very long time without a possible solution in sight.
What are the arrangements to settle Inter-state water disputes?
• Schedule 7 of Constitution
o It distinguishes between the use of water within a State and the purpose of regulating interstate waters.
o Entry 56 in Union List gives the Union Parliament the power to formulate laws and mechanisms for regulating Interstate rivers.
o Entry 17 in State List, States retain autonomy regarding water utilisation for purposes such as water supply, irrigation and canals, drainage and embankments, water storage and water power subject to provisions of Entry 56 of List 1.
• Article 262
o In case of disputes relating to waters, Parliament may by law provide for the adjudication of any dispute or complaint with respect to the use, distribution or control of the waters of, or in, any inter-State rivers.
o Parliament may, by law also provide that neither the Supreme Court nor any other court shall exercise jurisdiction in respect of any such dispute or complaint as mentioned.
• River Board Act, 1956
o The river Boards are supposed to advise on the Inter-state basin to prepare development scheme and to prevent the emergence of conflicts. Till date, no River Board has been created.
• Inter-State Water Dispute Act, 1956
o If a particular State or States approach the Union Government for the constitution of the tribunal.
o Central Government should try to resolve the matter by consultation among the aggrieved States and in case, consultation does not work, then the Union Government may constitute the tribunal.
Why Inter-state water disputes continue to persist?
• The legislative powers concerning water have been distributed between the Union and the State Governments. This approach of imprecise distribution of power between the Union and the States, has created a Federal-Jurisdictional ambiguity.
• Absence of effective authority for enforcing the orders of tribunals. The Tribunal can only make an award and cannot make it binding.
• Article 262 provides that the Parliament may by law prevent the Supreme Court or any other Court from exercising jurisdiction in inter-State water disputes. However, under Article 136, the Supreme Court can hear appeals against the orders of Tribunals.
• There have been excessive delays in establishing tribunals and making awards.
• There is a lack of data regarding water flows, seasonal variations which results in ambiguities regarding availability of water, surplus water for sharing etc.
What should be the way forward?
• The Sarkaria Commission has suggested that the awards of the tribunals be given the same weight as a Supreme Court Judgment.
• Leverage the Inter-State Council to enable it to play a more active role in settlement of such disputes.
• Few experts have recommended for mediation, (a third party acts as an intermediary between the parties in conflict), can also be explored as a possible option for successful resolution of disputes. Example of role of the World Bank as a mediator in the Indus Water Treaty between India and Pakistan is quoted as a success of this model.
• Infrastructure should be created for better collection of the data related to inter-State river basins. Better data will provide clear picture regarding availability of waters, seasonal variations and help in the equitable distribution of water among the States.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com