Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
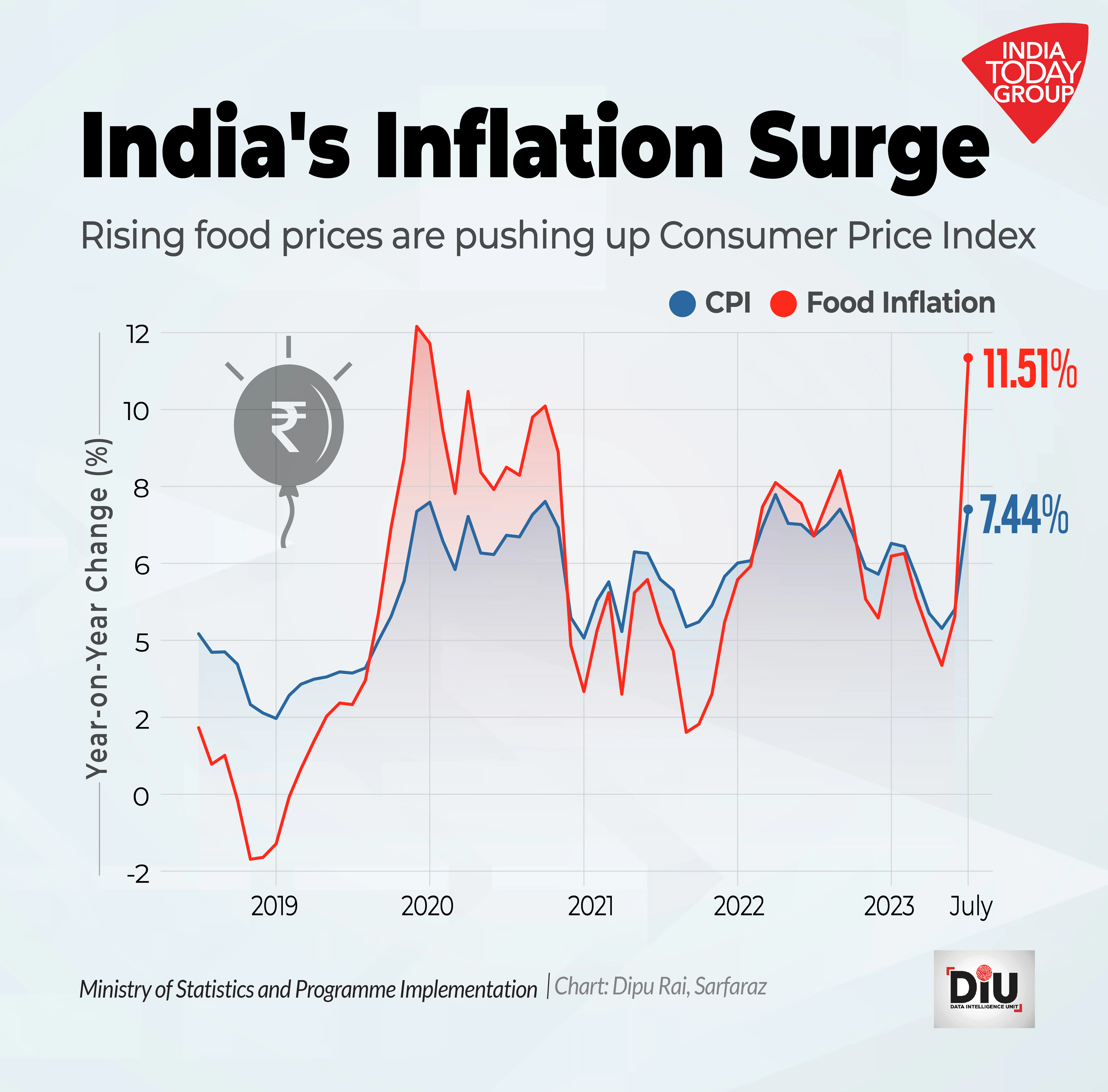
India’s Food Inflation
News: Recently, An ICRIER paper, “Tackling Food Inflation: Is restricting exports and imposing stocking limits the optimal policy?” discusses the causes of high food inflation in India, and government actions, and suggests alternative solutions.
What is ICRIER?
• The Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER) is one of India’s premier economic think tanks.
• Established in 1981, ICRIER is an autonomous, policy-oriented, not-for-profit, economic policy think tank. It aims to provide policy advice to effectively deal with external economic shocks
What is Current status of Food inflation in India?
• India’s retail inflation in August 2023 is at 6.83%, exceeding the desired ceiling of 6%. Food and beverages contribute significantly, making up 57% of retail inflation. Food inflation has risen sharply to 9.94%, impacting overall retail inflation.
What are the causes of Food inflation in India?
• Supply Shocks - The current food inflation is largely supply shock-driven. Short-term supply shocks, such as poor weather conditions, have occurred. Supply-chain disruption due to the pandemic, RussiaUkraine war also is one of the reason.
• Rising Cost of Production - Rise in cost of production and Minimum Support Price (MSP) are the main drivers of cereal inflation.
• Increased Demand - Increased income and dietary variety increase the market for food items and add to inflationary pressures.
• High international prices
• Increased transportation costs and increase in prices of key inputs also contribute to food inflation.
What are the recent initiatives taken to contain food inflation?
• Wheat Export Ban in May 2022
• Rice Export Restrictions – Halted exports of broken rice (September 2022) and imposed export ban on non-basmati white rice (July 2023)
• Rice Export Duties - Imposed 20% export duty on parboiled rice (July 2023)
• Export Duty on Onion - Imposed a substantial 40% export duty on onions (August 2023)
Key recommendations:
• Reduce import duties on edible oils and wheat. Import prices should ideally be lower than MSP.
• Build buffer stocks for volatile vegetable staples (TOP)
• Expand cold storage infrastructure and use solar energy for storage
• Support Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) and farmer cooperatives. Use schemes like “Operation Greens” to support FPOs and processing facilities.
• Promote processing of at least 10% of fresh produce
• Invest in R&D to enhance productivity and climate-resilient farming practices
• Increase irrigation coverage through micro-irrigation infrastructure

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com