Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
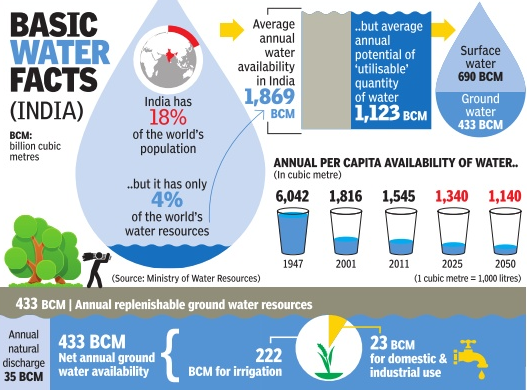
Groundwater in India
News: India receives 4,000 billion cubic metres (BCM) of freshwater annually through precipitation, but only 1,123 BCM of it is usable.
Background:
• Growing domestic, industrial and agricultural demand is increasing the stress on groundwater resources. We need to urgently address this pressure, starting with irrigation water use.
Groundwater Extraction in India
• India uses the most groundwater in the world, accounting for approximately 25% of the global groundwater extraction.
• Growing domestic, industrial and agricultural demand is increasing the stress on groundwater resources.
• For example, India is dangerously falling under the category of a water-scarce country. India gets 1,486 cubic metres (1 cubic metre = 1,000 litres) per capita of freshwater every year.
• A country is officially water-scarce when the per capita availability is less than 1,000 cubic metres per annum.
What are the causes of High groundwater extraction in India?
• Inadequate and erratic rainfall seen in different states of the country
• Increase in Demand attributed to factors such as rise in population, growing urbanisation (led to deforestation) and rise in industrial activities has decreased water quality.
• Increase in dependence on Groundwater by farmers due to unavailability of surface irrigation. More than 60% of irrigation requirement are met by groundwater.
• Due to Green Revolution, water intensive crops could be grown in water deficit region. For instance, the case of paddy in North and North West India.
• As Water is a state subject, forming a comprehensive law is under primary domain of states. Ineffective management and weak regulations encourage overexploitation of groundwater.
• Water and Electricity policies of different states (Free electricity, subsidized electricity, Higher MSP for Rice, Wheat) all have contributed to increased groundwater extraction.
What are the impact of Groundwater extraction?
• Land subsidence - When groundwater is pumped out, the soil above it can sink or collapse, causing
damage to buildings and infrastructure.
• Lowering of the Water Table - Excessive pumping can lower the groundwater table, and cause wells to no longer be able to reach groundwater.
• Increased Costs - As the water table lowers, the water must be pumped farther to reach the surface, using more energy and consequently more costs.
• Water quality degradation – It reduces the natural filtering capacity of the soil, allowing contaminants to reach the aquifer. It can also cause saltwater intrusion in coastal areas, making the groundwater unfit for drinking or irrigation.
• Polar drift - Groundwater extraction can also affect the Earth’s rotation by changing the distribution of mass on the planet.
• Groundwater-dependent ecosystems - Groundwater extraction can reduce the discharge of groundwater to surface water, which decreases the flow in rivers and streams and affects the habitats and biodiversity of aquatic organisms.
What are steps taken by government for Groundwater management?
• Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) - This is a World Bank-supported program to improve groundwater management in seven states that have the highest rates of groundwater depletion.
• Master Plan for Artificial Recharge to Groundwater in India by Central Ground Water Board.
• Jal Shakti Abhiyaan, 2019 is a time-bound, mission-mode water conservation campaign.
• Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) – Watershed development, surface minor irrigation.
• National Water Policy, 2012
Way Forward
Increasing reliance of Farmers on Groundwater can be minimized in following ways
• Increase in yield of crops other than paddy
• Incentivising water-saving crops
• Dis-incentivising water-guzzling crops
• Method such as Volumetric water pricing where a fix quota of Water allotment rights (WAR) are given to farmers. Those who use water below WAR can be given incentives at the defined rate.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com