Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
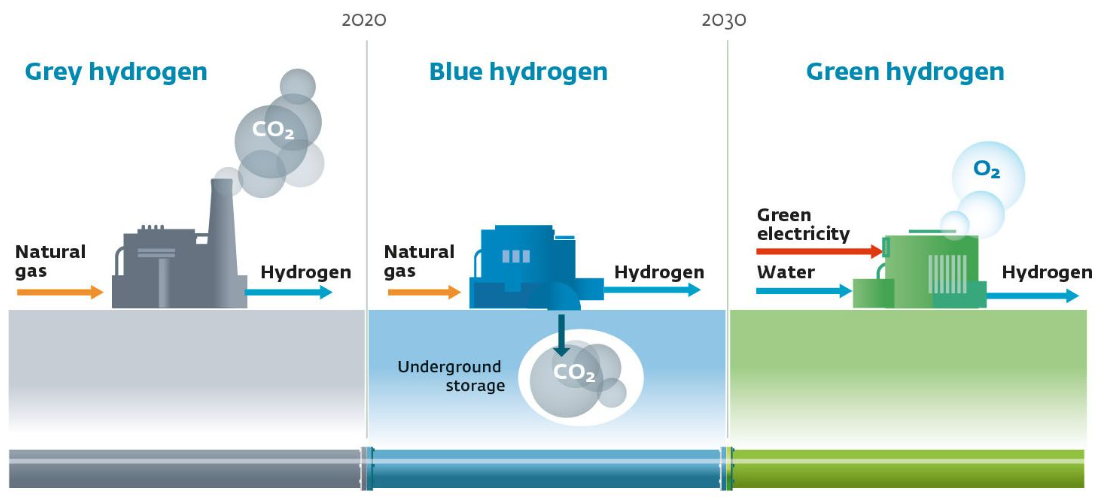
Green Hydrogen in the Steel Sector
News: Recently, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has issued guidelines, named “Scheme Guidelines for
Implementation of Pilot Projects for use of Green Hydrogen in the Steel Sector under the “National Green Hydrogen
Mission”.
• It aims to replace fossil fuels and fossil fuel-based feedstock with Green Hydrogen and its derivatives.
• The Scheme will be implemented till FY 2029-30.
Key Highlights of the Guidelines:
Thrust Areas:
• Three areas have been identified as thrust areas for the pilot projects in the steel sector. These are:
1. Use of Hydrogen in Direct Reduced Ironmaking process
2. Use of Hydrogen in Blast Furnace
3. Substitution of fossil fuels with Green Hydrogen in a gradual manner.
• The scheme will also support pilot projects involving any other innovative use of hydrogen for reducing carbon emissions in Iron and Steel Production.
Blending Approach:
• Steel plants are encouraged to begin by blending a small percentage of green hydrogen in their processes and gradually increase the blending proportion as cost economics improves and technology advances.
Incorporation in New Plants:
• Upcoming steel plants are expected to be capable of operating with green hydrogen to participate in future global low-carbon steel markets.
• The scheme also supports greenfield projects aiming at 100 green steel.
What are the Challenges in Adopting Green Hydrogen in Steel Plants?
Technological Adaptation:
• Transitioning from traditional steelmaking processes to hydrogen-based methods requires significant technological adaptation. Existing steel plants may need to undergo substantial modifications or even complete redesign to accommodate hydrogen as a primary reducing agent.
Infrastructure Requirements:
• The production, storage, and transportation of hydrogen necessitate significant infrastructure development. Establishing hydrogen production facilities, storage tanks, and distribution networks adds complexity and cost to steel plant operations.
Cost Implications:
• Adopting hydrogen-based processes may incur higher initial capital costs compared to conventional methods. Investment in new equipment, infrastructure, and technology, as well as ongoing operational expenses, can pose financial challenges for steel producers, especially in the face of fluctuating market conditions.
Supply Chain Constraints:
• Ensuring a reliable supply chain of hydrogen, including sourcing raw materials and maintaining consistent production levels, is crucial for uninterrupted steel plant operations. Dependence on external suppliers and potential supply chain disruptions may present logistical challenges.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
Battle Preparedness and Efficiency Test (BEPT) is a mandate for all personnel up to 45 years of age once in every quarter. One has to run 5 km in 25 minutes for up to 30 years of age and for those above 30 years up to 40, additional 2 minutes are given.
• Although hydrogen-based steel production offers the potential for significant carbon emissions reductions, capturing and storing CO2 emissions generated during the process remains a challenge.
• Developing cost-effective CCS technologies compatible with steel plant operations is critical for achieving net-zero emissions targets.
What are the Efforts to Promote Green Steel Production?
International Collaborations: At the 28th Conference of Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on
Climate Change, India announced its partnership with Sweden under the LEAD-IT initiative which had a focus on industrial Decarbonisation, specially the steel sector.
• Swedish company SSAB was the first globally to produce steel through hydrogen back in 2018.
• Yet another Swedish company, H2-Green Steel, is also planning to roll out its first batch of green steel using hydrogen by 2025.
• Similar initiatives are being taken by Nippon Steel in Japan and other competitors in France and Germany.
Domestic Companies:
• Domestically, companies like Tata Steel and ArcelorMittal Nippon Steel India have started taking initiatives towards using hydrogen.
• In January 2024, ArcelorMittal Nippon Steel India signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the Maharashtra government, proposing to establish a 6 million tonnes per annum green steel plant in Maharashtra that plans to use hydrogen instead of coal.
Government Schemes:
• Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) Scheme: PAT Scheme incentivizes the steel industry to reduce energy consumption.
• Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga Project to promote the manufacturing of Green steel.
• Steel Scrap Recycling Policy, 2019: Steel Scrap Recycling Policy, 2019 enhances the availability of domestically generated scrap to reduce the consumption of coal in steel making.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com