Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Global Gender Gap Report 2023
News: Recently, 17th edition of the Global Gender Gap Report 2023 has been released by the World Economic Forum (WEF), evaluating the status of Gender Parity across 146 countries.
What is Global Gender Gap Report?
• The Global Gender Gap report 2023 is a publication by the World Economic Forum (WEF) that benchmarks the progress towards gender parity across 146 countries and four dimensions: economic participation and opportunity; educational attainment; health and survival; and political empowerment.
• The report ranks countries based on their gender gap scores, which range from 0 (no parity) to 1 (full parity).
Key Findings:
• The report shows that the world would take 131 years to close the overall gender gap between men and women at the current rate of progress.
• The report also highlights that the Covid-19 pandemic has caused major setbacks for gender equality, especially in the economic and political spheres.
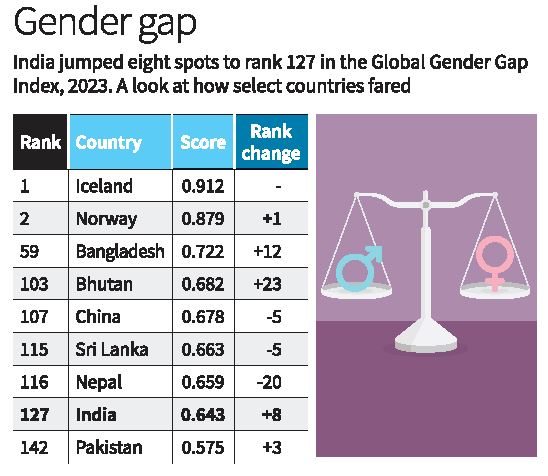
• The most gender-equal country in 2023 is Iceland, with a score of 0.912, followed by Norway, Finland, New Zealand and Sweden.
• The least gender-equal country is Yemen, with a score of 0.462, followed by Iraq, Pakistan, Syria and Congo.
• United states rank 43rd, with a score of 0.748.
How has India fared in the Global Gender Gap Report 2023?
• According to the Global Gender Gap report 2023, India has improved its rank by eight places to 127 out of 146 countries in terms of gender parity. India has closed 64.3% of the overall gender gap, marking a partial recovery towards its 2020 parity level.
• India has achieved equality in enrolment across all levels of education, ranking 26 on the sub-index with a score of 14.
• However, India has reached only 36.7% parity on economic participation and opportunity, with low shares of women in senior positions and technical roles.
• India has also registered 25.3% parity on political empowerment, with women representing 15.1% of parliamentarians, the highest for the country since 2006. India also has a female President who assumed power following the 2022 Presidential election. India has achieved representation of women of over 40% in local governance, which is among the highest in the world.
What are some of the challenges for Gender equality in India?
• Patriarchy - India has a patriarchal culture that values men over women and assigns them different roles and expectations. Patriarchy also influences social norms, laws, and institutions that discriminate against women and limit their opportunities.
• Education - Women and girls often face barriers to access quality education, such as poverty, early marriage, domestic violence, and lack of sanitation facilities. As a result, they have lower literacy rates, lower enrolment rates, and higher dropout rates than men and boys.
• Occupation - Women have less participation and representation in the formal labor market than men. They face discrimination in terms of wages, benefits, promotions, and working conditions. They also have less access to skills training, entrepreneurship opportunities, and financial resources.
• Preference of sons - India has a strong preference for sons over daughters, which leads to practices such as sex-selective abortion, female infanticide, neglect of girls’ health and nutrition.
• Financial autonomy - Women have less control over their own income and assets than men.
What are some of the initiatives taken by government of India to promote Gender Equality?
• Some of the laws made by government such as Equal Remuneration Act, 1973; Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005; Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013; Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006.
• Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
• Mahila Shakti Kendra (2017) – To empower rural women with skill development, digital literacy, health and nutrition.
• Rashtriya Mahila Kosh (RMK): This is an apex micro-finance organization that provides micro-credit at concessional terms to poor women for various livelihood and income generating activities.
• Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana – maternity benefits to pregnant and lactating mothers.
• Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana – It mandates that the house should be registered preferably in the name of the woman or jointly with her husband.
• Pradhan Mantri Ujjawala Yojana, Sukanya Samriddhi scheme, One-stop center scheme.
• Stand-up India scheme – The scheme mandates that loans be facilitated to at least 1 women borrower per bank branch for setting up greenfield enterprises in the non-farm sector.
• Jan Dhan accounts to promote financial inclusion for women.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com