Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
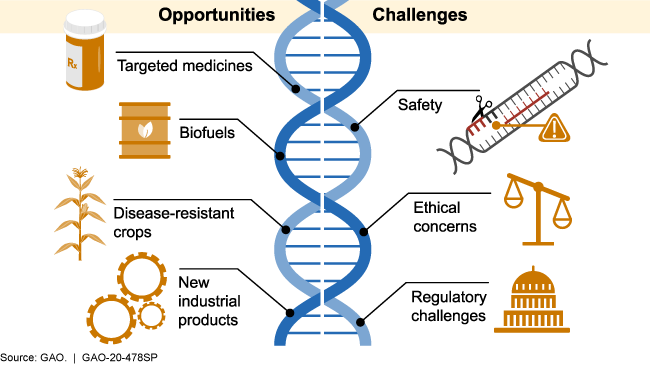
Genome Editing
News: Recently, the Government has allowed genome-edited plants without the cumbersome GMO (Genetically Modified Organisms) regulation at the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
• The government has exempted Site Directed Nuclease (SDN) 1 and 2 genomes from Rules 7-11 of the Environment Protection Act, thus allowing it to avoid a long process for approval of GM crops through the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
• The Institutional BioSafety Committee (IBSC) under the Environment Protection Act would now be entrusted to certify that the genome edited crop is devoid of any foreign DNA.
About Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee:
• It functions under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
• It looks into the activities involving large scale use of hazardous microorganisms and recombinants in research and industrial production from environmental perspective.
• It is also responsible for the appraisal of proposals relating to the release of genetically engineered organisms and products into the environment including experimental trials.
About Genome Editing:
• Genome editing (also called gene editing) is a group of technologies that give scientists the ability to change an organism's Deoxy-Ribonucleic Acid (DNA).
• These technologies allow genetic material to be added, removed, or altered at particular locations in the genome.
How is Gene editing different from GMO development?
• Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) involves modification of the genetic material of the host by introduction of a foreign genetic material.
• In the case of agriculture, soil bacteria is the best mining source for such genes which are then inserted into the host genome using genetic engineering.
• The basic difference between genome editing and genetic engineering is that while the former does not involve the introduction of foreign genetic material, the latter does.
• In the case of agriculture, both the techniques aim to generate variants which are better yielding and more resistant to biotic and abiotic stress.
Regulatory Issues:
• Across the world, GM crops have been a topic of debate, with many environmentalists opposing it on the grounds of bio safety and incomplete data.
• In India, the introduction of GM crops is a laborious process which involves multiple levels of checks. Only Bt Cotton has thus far crossed the regulatory red tape.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com