Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Ethics of Climate Engineering
News: The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in its report on the Ethics of Climate Engineering emphasized the importance of including vulnerable, neglected, and marginalized individuals as valuable stakeholders in policy decisions regarding climate engineering.
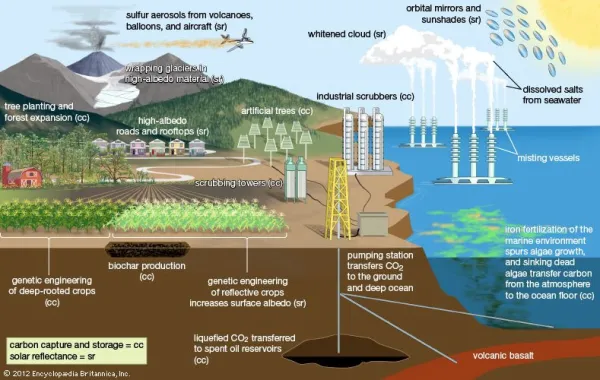
What is Climate Engineering?
• Climate engineering, also known as geoengineering, is the intentional large-scale intervention in the Earth’s climate system to counter climate change.
• It includes techniques to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and technologies to rapidly cool the Earth by reflecting solar energy back to space.
There are two main types of climate engineering:
• Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR): This involves techniques like reforestation, biochar production, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), direct air capture and carbon storage, and enhanced weathering. These techniques aim to capture and sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
• Solar Radiation Management (SRM): This refers to technologies proposed to rapidly cool down Earth’s temperature. Proposals include simulating the cooling effects of volcanic eruptions, and enhancing the reflectivity of marine clouds. These techniques aim to reflect some of the sunlight back into space.
Ethical Issues highlighted in the report:
• Climate engineering methods may pose a 'moral hazard' by giving stakeholders a reason to avoid reducing fossil fuel use.
• Potential risk of climate engineering diverting resources from crucial emission reduction and adaptation efforts.
• Climate engineering tools may be exploited for military or geopolitical purposes, necessitating strengthened global governance efforts.
• Climate engineering could be pushed by corporations as a favored response to tackling global warming while fostering business investments and economic growth.
Key recommendations:
• States should introduce legislation regulating climate engineering to minimize potential harm.
• Scientific research must adhere to ethical standards consistent with international law.
• Countries must assess and consider the transboundary impact of their climate engineering decisions and an open and responsible collaboration between countries is critical for effective global governance of climate engineering

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com