Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
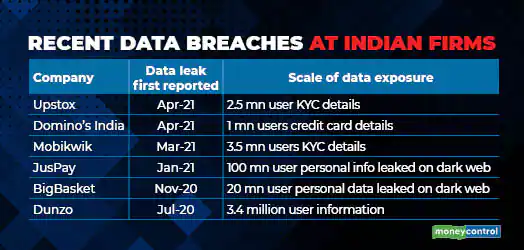
CoWin Data Leak
News: The recent media reports about the CoWin data leak are no doubt disconcerting, but what is even more so is the government’s response to them.
Why is recent CoWin data leak a worry?
• General acceptance amongst the crowd that phone or Aadhar numbers may already be out there with hundreds of entity anyway.
• Same old statements and defence from keepers of the system argue that the security and privacy safeguards deployed are foolproof because they use “state-of-the-art best practices”
What are concerns associated with Data security in India?
• Misuse of leaked personal data pertaining to Aadhar, DOB, phone details for illegally profiling voters and influencing them or for profiling people for predatory pricing.
• Despite the rising number of cyberattacks and the urgent calls for stronger cybersecurity measures, India currently lacks a comprehensive national cybersecurity law.
• Lack of comprehensive Personal Data protection law. India’s Personal data protection bill, 2019 was withdrawn recently. Data protection in India remains under IT act, 2000, which only provides for punishment in cases of negligent data handling.
• Most Indian internet users rely on foreign-owned social networking sites and hardware, creating unique national security challenges.
• The MIT Technology Review CyberDefense Index indicates India has a significant deficit in critical infrastructure, weak cybersecurity regulation, and limited national digital economy adoption, despite having a digital-forward government and one of the world’s largest IT-enabled service sectors.
How is Data security ensured in India?
• CERT-In - It is the national nodal agency that deals with cybersecurity threats in India.
• India relies on regulations within the Information Technology (IT) Act of 2000 and sector-specific regulations for data privacy and protection.
• India has a national cybersecurity policy that provides a framework for securing cyberspace in the country.
• India has established a digital public infrastructure (DPI), known as India Stack which ensures secure and privacy-respecting digital access to public and private services.
Why should India focus on Data security?
• India’s rapid digital transformation, especially in government services and the financial sector, necessitates a stronger focus on data security.
• Over 80 million Indian users were reportedly affected by data breaches in 2021.
• India witnessed over 674,000 cybersecurity incidents in just the first half of 2022, as reported by CERTIn.
• Despite the Supreme Court’s ruling in 2017 that privacy is a fundamental right, comprehensive data protection legislation is still missing in India.
What are examples of important Data breaches and Cyber-security attacks in India?
• AIIMS ransomware attack (2023), BFSI sector faced vulnerability attacks in first quarter of 2023.
• Air India Data breach (2021) - Air India disclosed that a cyberattack on its data processor, SITA, had compromised the personal data of 4.5 million passengers worldwide.
• Mobikwik data breach (2021), Upstox data breach (2021)
How nations worldwide ensure Data security?
• The European Union implemented the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which offers stringent guidelines for the collection, storage, and use of personal data. Post Brexit, the UK has incorporated UK GDPR.
• The USA does not have a comprehensive federal data protection law, but rather a patchwork of sectorspecific and state-level laws that regulate different aspects of data privacy and security
• China does not have a single comprehensive data protection law, but rather a collection of laws, regulations, standards, and guidelines that govern different aspects of data privacy and security.
What is the need of the hour?
• Comprehensive legal framework on Personal data protection on the lines of EU’s GDPR.
• A dedicated cyber-security ministry (like Australia) to oversee and respond to cybersecurity threats.
• Invest in skilling and up-skilling in cyber-security domains.
• Adopt a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) approach, which assumes that no users or devices are trustworthy by default, regardless of their location or network, can help bolster security.
Source – Economic Times, TOI, Indian Express

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com