Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Solar waste in India
News: India’s solar waste could reach 600 kilotonnes by 2030 according to a study published by Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) in collaboration with the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
Key Findings:
Waste Generation: India’s installed 66.7 gigawatt (GW) capacity, as of FY23, has generated about 100 kilotonnes (kt) of cumulative waste, which will increase to 340 kt by 2030. This volume will increase 32 times by 2050 resulting in about 19000 kt of cumulative waste.
States Contribution: Around 67 percent of this waste is expected to be generated in five states: Rajasthan, Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh.
What is solar waste?
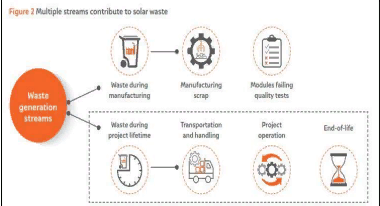
Solar waste refers to the waste generated during the manufacturing of solar modules and waste from the field (project lifetime).
Manufacturing involves two streams of waste, including the scrap that’s produced and the waste generated from PV modules failing quality tests.
Waste from the field involves three streams of waste. Waste generated during transporting and handling — the damaged modules are considered as waste. Waste produced due to the damage incurred by solar modules during their lifetime. When the modules reach their end-of-life and are not usable anymore.
The study only focused on waste from the field (project lifetime) category and excluded waste generated during manufacturing.
What are the recommendations?
The policymakers should maintain a comprehensive database of the installed solar capacity, which would help in estimating solar waste in the following years.
The MoEFCC must issue guidelines for collecting and storing solar waste. Additionally, it should also promote safe and efficient processing of stored waste.
Solar cell and module producers should start developing waste collection and storage centers to adhere to the responsibilities assigned in the E-waste Management Rules 2022.
Policymakers should incentivize recyclers, and push stakeholders to effectively manage the growing solar waste.
Does India have a solar waste management policy?
India does not currently have a specific solar waste management policy in place.
The management of waste generated from solar PV modules, panels and cells is part of the Electronic Waste Management Rules 2022.
o The rules mandate solar PV module and cell producers to store the waste generated from solar PV modules and cells up to 2034 – 2035 as per the guidelines laid down by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
o The rules also mandate the filing of annual returns on the e-waste management portal up to 2034 –2035.
o Every recycler of solar PV modules and cells shall be mandated for the recovery of materials as laid down by the CPCB.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com