Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Climate Smart Agriculture
Context: Recently, an editorial was covered on Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) which recommended a way to address Climate change and improve farming.
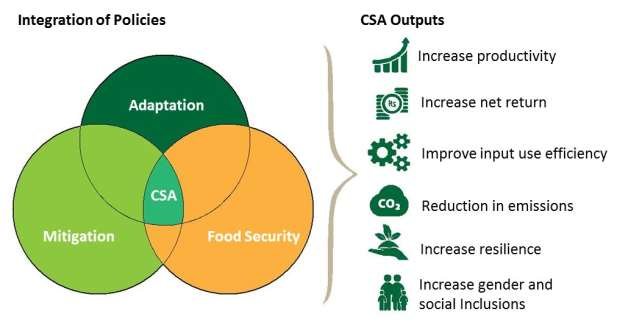
What is CSA?
• Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) is an integrated approach to managing landscapes—cropland, livestock, forests, and fisheries—that addresses the interlinked challenges of food security and climate change.
• According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), CSA aims to enhance the capacity of the agricultural systems to support food security, incorporating the need for adaptation and the potential for mitigation into sustainable agriculture development strategies.
CSA aims to simultaneously achieve three outcomes
• Increased productivity: Produce more and better food to improve nutrition security and boost incomes, especially of 75 percent of the world’s poor who live in rural areas and mainly rely on agriculture for their livelihoods.
• Enhanced resilience: Reduce vulnerability to drought, pests, diseases, and other climate-related risks and shocks; and improve capacity to adapt and grow in the face of longer-term stresses like shortened seasons and erratic weather patterns.
• Reduced emissions: Pursue lower emissions for each calorie or kilo of food produced, avoid deforestation from agriculture, and identify ways to absorb carbon out of the atmosphere.
What are benefits of CSA?
• Improving Agricultural Productivity
• Building Resilience: CSA helps fortify agricultural infrastructure against the destructive effects of global warming. This includes taking measures to minimize susceptibility to climate-related threats like floods, droughts, or extreme heat.
• Reducing Environmental Impact: One of the primary goals of CSA is to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere because of farming activities, including methane emissions from livestock, paddy rice cultivation, and synthetic fertilizer use.
• Boosting Farmers’ Livelihoods: Farmers who adopt CSA practices often see a rise in income while also helping to combat climate change and strengthen global food security.
• Creating New Business Opportunities: CSA helps build more sustainable food systems that protect the environment, improve smallholder livelihoods, and create new business opportunities.
• Building Household Resilience: With the right resources, smallholder farmers can not only produce more, but also higher quality crops.
Challenges that may arise in implementing CSA practices:
• High Cost of Inputs: The cost of inputs required for CSA practices can be high, which might pose a financial burden on farmers.
• Limited Knowledge about CSA: Farmers may lack the necessary knowledge and understanding about CSA practices, which can hinder their adoption.
• Youth Migration from Rural Areas: The migration of young people from rural to urban areas can lead to a shortage of labor in farming communities, making it difficult to implement CSA practices.
• Uncertain climate projections make it difficult for farmers to implement CSA practices.
• Recuperating Costs: It might be challenging for farmers to recuperate their costs for implementing CSA and make the switch profitable.
• Novelty and Limited Scope: CSA is relatively new, particularly in countries like India. For example, the scope of initiatives like precision farming is still limited.
Government of India initiatives:
• National Innovation on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) – Initiated by ICAR in 2011 the project seeks to increase the resilience of Indian agriculture.
• The National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC) – It was formed to cover costs of climate change adaptation for Indian states which are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change.
• The National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) - It includes initiatives like Soil Health Card, Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana, Mission Organic Value Chain Development, Rainfed Area Development, National Bamboo Mission, and Agro-Forestry.
• Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, PM Fasal Bima Yojana, Bio-tech Kisan, Climate Smart Villages

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com