Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
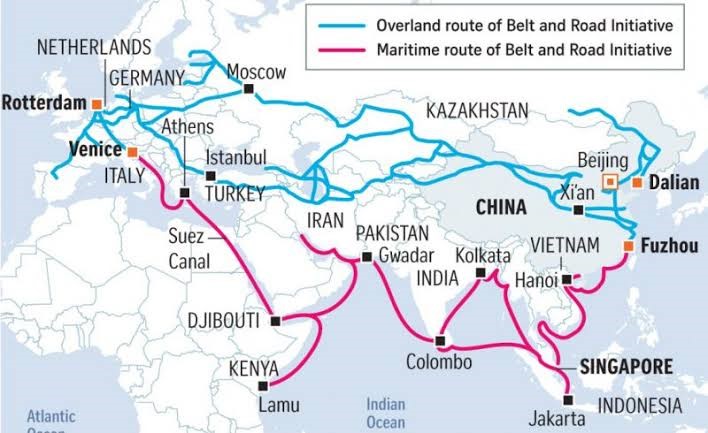
10 years of Belt and Road initiative
News: The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), led by Chinese President Xi Jinping, marked its 10th anniversary.
What is BRI?
• The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI, or B&R), also known within China as the One Belt One Road (OBOR / 1B1R), is a global infrastructure development strategy adopted by the Chinese government in 2013. The initiative aims to invest in more than 150 countries and international organizations.
• The BRI, often referred to as the New Silk Road, is a colossal network of infrastructure projects designed to facilitate trade, economic development, and cultural exchange.
• It consists of two primary components: i) The Silk Road Economic Belt, which stretches overland across Asia and ii) The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, which traverses the seas.
What are the benefits of BRI for China and other countries?
For China
• The BRI serves as a way for China to develop new trade linkages, cultivate export markets, boost Chinese incomes, and export China’s excess productive capacity.
• BRI increases China’s influence in participating countries and on the world stage.
• Promotes the use of the Chinese yuan (RMB) in international trade and finance.
• BRI projects secure access to crucial energy resources for China.
• BRI facilitates technology transfer and knowledge exchange between China and its partners.
For other countries
• The BRI has played a vital role in addressing the global infrastructures gap through the construction of modern highways, airports, high-speed railways, bridges, power generation (hydropower), and industrial parks. This has enhanced connectivity and economic growth between Asia, Europe, and Africa.
• Numerous studies conducted by the World Bank have estimated that BRI can boost trade flows in 155 participating countries by 4.1 percent, as well as cutting the cost of global trade by 1.1 percent to 2.2 percent, and grow the GDP of East Asian and Pacific developing countries by an average of 2.6 to 3.9 percent.
• Examples of Projects – 1. Pakistan (CPEC), Laos (China-Laos railway), 3. Greece (The Piraeus Port project has turned Greece into a major transport hub, increasing trade and creating jobs) 4. Sri Lanka (Hambantota port)
Concerns around BRI projects:
• Lack of transparency in BRI projects, particularly related to debt and loan conditions. BRI infrastructure project has encountered major implementation problems, such as corruption scandals, labour violations, environmental hazards, and public protests..
• Chinese state-owned enterprises dominate BRI investments, limiting competition and opportunities for other companies.
• China is criticized for practising “debt-trap diplomacy,” where it lends money to countries like Sri Lanka and Zambia, who struggle to repay, leading to China acquiring strategic assets or political concessions.
• Some BRI projects face delays and challenges, leading to questions about the feasibility and impact of China’s ambitious strategy.
What are alternative projects to challenge to the Dominance of China?
• G7’s Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII) - This is an infrastructure partnership that aims to address infrastructure gaps of low- to middle-income countries.
• India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) initiative during the recent G20 summit.
• International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) for connecting India to the Middle East and Russia.
• Blue dot network - A multi-stakeholder initiative by the US, Japan, and Australia to promote high-quality standards for global infrastructure development.
• India’s “IDEAS” plan - India’s counter to BRI, supported by Lines of Credit (LOCs) to countries in Asia, Africa, CIS, and Latin America. It includes initiatives like IMEC and INSTC.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com