Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
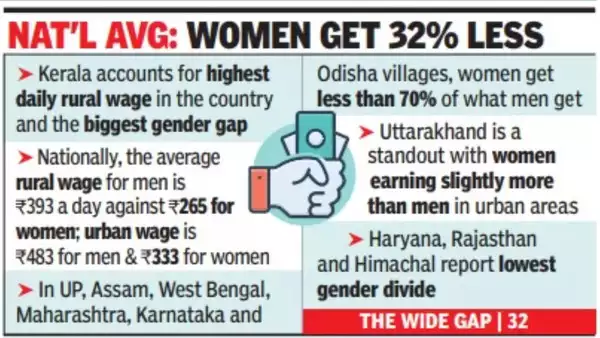
Rural Wage Disparities
News: Recent data from the Reserve Bank of India highlights stark differences in rural wages across different states in India.
Key Findings:
• FY 2021-22 (Covid-19 challenges faced by rural economy), FY 2022-23 (High inflation rates, increased interest rates, low growth) These factors heavily impacted job opportunities and income stability in rural areas across the nation.
• Rural wages in Madhya Pradesh for agricultural and non-agricultural workers are significantly below the national average standing at Rs 229.2 and Rs 246.3 daily, respectively.
• Kerala boasts the highest wages across various sectors, with rural farm workers earning Rs 764.3 per day.
• Despite some wage growth peaks in 2022-23, rural income prospects remained subdued, stagnating the real rural wage growth and indicating an incomplete recovery in the unorganized segment of the economy. For instance, MGNREGA job demand dipped but remained higher than pre-pandemic levels in 2022-23, signaling an incomplete recovery, especially in the unorganized sector.
What are the Major Factors responsible for Wage disparities in India?
• Regions or states with varying levels of economic development showcase substantial wage differences. Advanced industrial regions tend to offer higher-paying non-agricultural jobs compared to agrarian-centric areas.
• Changes in the productivity of various sectors, notably the increase in agricultural and non-agricultural productivity, have contributed to the structural transformation process and rural-urban wage convergence in India.
• Diverse state-level policies regarding minimum wages, labor regulations, and social security schemes also create wage disparities. States with stringent labor laws may offer higher wages but could also face fewer job opportunities.
• Variations in the cost of living, housing expenses, and other essential amenities directly impact wage disparities. Areas with higher living standards or higher costs of necessities often offer higher wages to compensate.
• Education System: A poor education system can contribute to wage inequality, as it may not provide equal opportunities for everyone.
• Inconsistencies in the unorganized sector can contribute to wage inequality.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com