Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
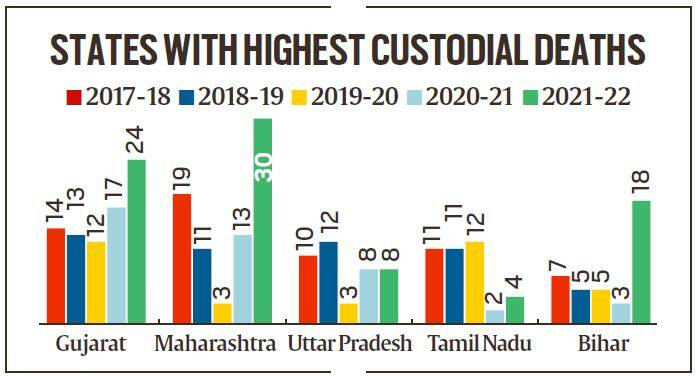
Custodial Deaths
News: According to the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) in the last five years, the highest number of custodial deaths have been reported in Gujarat at 80.
What are Custodial Deaths?
Custodial death is a death that occurs while a person is in the custody of law enforcement officials or in a correctional facility. It can occur due to various causes such as use of excessive force, neglect, or abuse by the authorities.
According to the Law commission of India, the crime by a public servant against the arrested or the detained person who is in custody amounts to custodial violence.
What are reasons for Custodial Deaths?
India does not have anti-torture legislation and hasn’t criminalized custodial violence.
The use of excessive force including torture to target criminals.
Lengthy, expensive formal processes followed by courts dissuade the poor and the vulnerable.
Although India has signed the United Nations Convention against Torture in 1997 its ratification still remains.
Poor training or lack of accountability among law enforcement officials.
Inadequate or substandard conditions in detention centers.
Underlying health conditions or pre-existing medical conditions that are not adequately addressed or treated while in custody.
What are provisions available regarding Custody?
Protection from torture is a fundamental right enshrined under Article 21 (Right to Life) of the Indian constitution.
Article 22 provides “Protection against arrest and detention in certain cases”
Primary responsibility of State governments to ensure protection of human rights as Police and public order fall under State list according to 7th Schedule of Indian Constitution.
Section 41 of Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC) was amended in 2009 to include safeguards so that arrests and detentions for interrogation have reasonable grounds and documented procedures, arrests are made transparent to family, friends and public, and there is protection through legal representation.
Sec 330 & 331 of the Indian Penal Code 1860 provides punishment for injury inflicted for extorting confession. Crime of custodial torture against prisoners can be brought under Sec 302, 304, 304A, and 306 of IPC.
Section 25 of the Indian Evidence Act provides that a confession made to the police cannot be admitted in Court. Section 26 of the Act provides that a confession made to the police by the person cannot be proved against such person unless it is made before the Magistrate.
Way Forward
It is responsibility of State to check that strict adherence is followed in human rights laws and regulations which includes prevention of torture and inhuman treatment of prisoners.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com