Ahmedabad
(Head Office)Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
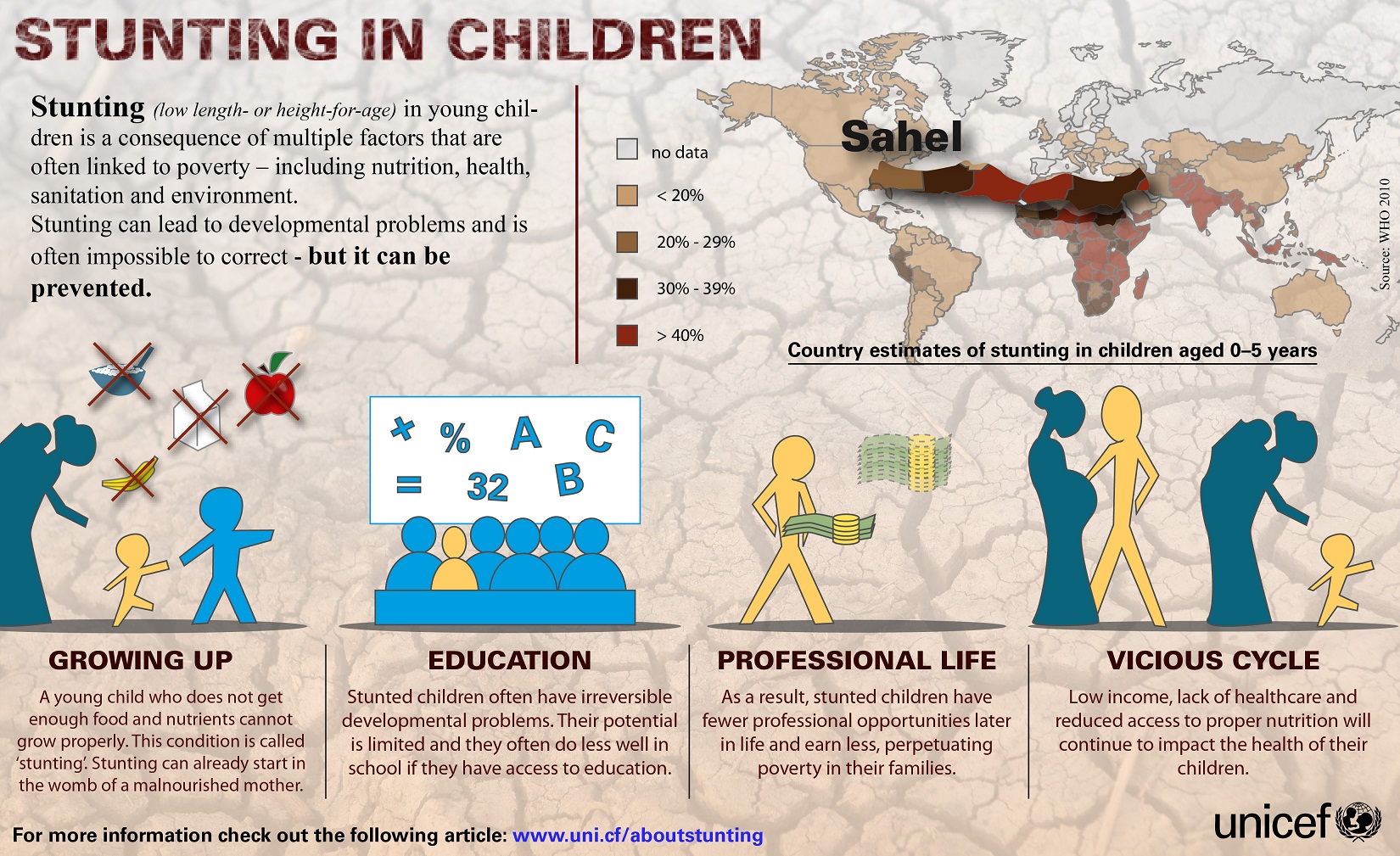
Child Stunting reduced, wasting and obesity remain concern
News: According to UNICEF, WHO, and World Bank Joint Malnutrition Estimates, Child stunting in India has improved but child wasting and Obesity in children remain a sign of worry.
Key Findings:
The Joint Malnutrition Estimates (JME) released by UNICEF, WHO and the World Bank revealed that India recorded 1.6 crore fewer stunted children under five years in 2022 as compared to 2012.
Stunting - This was accompanied by India's share of the global burden of stunting declining from 30% to 25% in the past decade.
Wasting - The prevalence of wasting in 2022 was 18.7% in India, with a share of 49% in the global burden of this malnutrition indicator.
Obesity - The prevalence of obesity marginally increased in a decade from 2.2% in 2012 to 2.8% in 2022.
Globally, stunting declined from a prevalence rate of 26.3% in 2012 to 22.3% in 2022.
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Targeting - There is insufficient progress to reach the 2025 World Health Assembly (WHA) global nutrition targets and the 2030 Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 2 targets; only about one-third of all NFHS-5 showed evidence of continued reduction of stunting and instances of underweight children, though anemia was disappointing.
It also showed an improvement in access to health services such as family planning, ante-natal care, deworming, and breastfeeding counselling.
Wasting is an outlier, with two-thirds of children at 12 or 24 months having wasting at birth or at one month of age. This means that children were born with very low weight for height and didn't recover even six months or 12 months later despite weight gain.
The JME estimates for stunting and obesity are based on country-level modelled estimates derived from primary sources, while for wasting, the estimates are based on national-level country prevalence data.
Key Recommendations:
Children suffering from severe wasting require early detection and timely treatment and care to survive.
More intensive efforts are required if the world is to achieve the global target of reducing the number of children with stunting to 89 million by 2030.
Regular data collection is critical to monitor and analyze country, regional and global progress on child malnutrition moving forward.
Government of India’s initiatives to tackle malnutrition:
Integrated Child Development Scheme and Anganwadi system – To provide supplementary nutrition and ration to pregnant and lactating mothers.
The National Food Security Act, 2013
National Nutrition Strategy (Niti Aayog) – Aims to reduce all forms of malnutrition by 2030.
POSHAN Abhiyaan
Mission POSHAN 2.0 – Seems to address the challenges of malnutrition in children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
Mission VATSALYA
Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana – Maternity benefits to eligible mothers (Pregnant and lactating)
Food Fortification – Rice, Iodine, Wheat, Edible Oil, Milk.

Address : 506, 3rd EYE THREE (III), Opp. Induben Khakhrawala, Girish Cold Drink Cross Road, CG Road, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad, 380009.
Mobile : 8469231587 / 9586028957
Telephone : 079-40098991
E-mail: dics.upsc@gmail.com
Address: A-306, The Landmark, Urjanagar-1, Opp. Spicy Street, Kudasan – Por Road, Kudasan, Gandhinagar – 382421
Mobile : 9723832444 / 9723932444
E-mail: dics.gnagar@gmail.com
Address: 2nd Floor, 9 Shivali Society, L&T Circle, opp. Ratri Bazar, Karelibaugh, Vadodara, 390018
Mobile : 9725692037 / 9725692054
E-mail: dics.vadodara@gmail.com
Address: 403, Raj Victoria, Opp. Pal Walkway, Near Galaxy Circle, Pal, Surat-394510
Mobile : 8401031583 / 8401031587
E-mail: dics.surat@gmail.com
Address: 303,305 K 158 Complex Above Magson, Sindhubhavan Road Ahmedabad-380059
Mobile : 9974751177 / 8469231587
E-mail: dicssbr@gmail.com
Address: 57/17, 2nd Floor, Old Rajinder Nagar Market, Bada Bazaar Marg, Delhi-60
Mobile : 9104830862 / 9104830865
E-mail: dics.newdelhi@gmail.com